Molecular and Crystal Structure of 2-Mercaptobenzoxazole
Sivajeyanthi P and Balasubramani K
Sivajeyanthi P and Balasubramani K*
Department of Chemistry, Government Arts College (Autonomous), Karur-639 005, Tamilnadu, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Balasubramani K
Department of Chemistry, Government Arts College (Autonomous), Karur-639 005, Tamilnadu, India.
E-mail: manavaibala@gmail.com
Received Date: January 29, 2016 Accepted Date: February 09, 2016 Published Date: February 13, 2016
Abstract
The crystal structure of the title compound has been determined by X-Ray diffraction. The compound crystallizes in the monoclinic, space group P21 with a=4.3465(4) Å, b=9.0294(10) Å, c=8.5669(11) Å and α=90°, β=90.074(4)° and γ=90°. The asymmetric unit contains one 2-mercaptobenzoxazole and the molecular structure of the compound is stabilized by strong intermolecular N--- H…S hydrogen bond.
Keywords
Single-crystal; X-ray study; 2-mercaptobenzoxazole; Intermolecular H-bond
Introduction
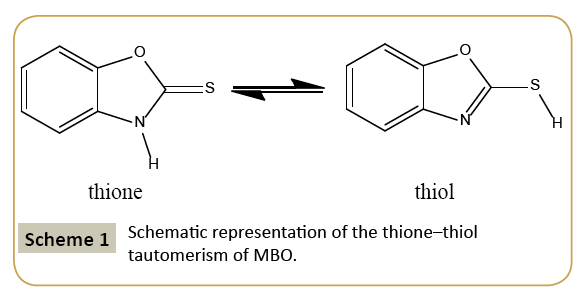
Heterocyclic thionate ligands have attracted interest as ligands with multifunctional coordination abilities caused by the presence of more than one heteroatom [1]. They can be regarded as monodentate or multidentate ligands and can also act as bridging ligands between metal centers. 2-mercaptobenzoxazole (Benzoxazole-2-thione) exhibits two tautomeric forms as shown in Scheme 1 [2]. As a result of this prototropic ability, nucleophilic attack of an alkyl halide on the 2-mercaptobenzoxazole could occur at either the N or the S atom, depending upon whether the molecule existed in the thiol or the thione form [3]. 2-Mercaptobenzoxazole (MBO) containing nitrogen and sulphur as electron donor atoms is used as a chelating-type flotation collector. Since S atom has strong interaction with the metal surface results in the formation of the insoluble complexes, many heterocyclic compounds like MBO have been developed for the different purposes [4] and its derivatives that contain mixed aliphatic–aromatic and alkoxyl-aromatic hydrocarbon chains in the phenyl ring as flotation collectors. To improve the efficiency of the flotation process on sulfide minerals, a new class of synthetic molecules such as MBO, has been used for higher selectivity of sulfide minerals, i.e., Pb, Zn and Cu bearing minerals [5,6].
Crystallisation
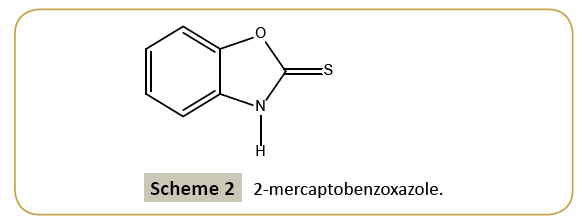
A hot methanolic solution (20 ml) of 2-mercaptobenzoxazole (35 mg, Aldrich) which has been warmed over a heating magnetic stirrer hotplate for a few minutes. The resulting solution was allowed to cool slowly at room temperature and the crystals of the title compound appeared after a few days (Scheme 2).
X-Ray crystallographic study
Crystals with dimensions 0.30 × 0.30 × 0.35 mm was used for X-ray data collection. All measurements were made on a Bruker Apex II Kappa CCD diffractometer [7] with graphite monochromated MoKα (0.071073 nm) radiation at 293 K using the ω scan technique. The structure was solved by SIR92 and refined using SHELXL-97 program [8,9]. The refinement was carried out by using full matrix least squares on F2. All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. All the hydrogen atoms were placed in the idealized locations and refined as riding model. All relevant information about the data collection and the refinement are presented in Table 1, bond lengths, angles are presented in Table 2 and hydrogen bonding geometry is given in Table 3.
| Crystal Data | |
|---|---|
| Formula | C7 H5 N O S |
| Formula Weight | 151.19 |
| Crystal System | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21 (No. 4) |
| a, b, c [Å] | 4.3465(4) 9.0294(10) 8.5669(11) |
| α β γ [°] | 90 90.074(4) 90 |
| V [3] | 336.22(6) |
| Z | 2 |
| D(calc) [g/cm3] | 1.493 |
| Mu(MoKα) [ /mm ] | 0.397 |
| F(000) | 156 |
| Crystal Size [mm] | 0.30 × 0.30 × 0.35 |
| Data Collection | |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| Radiation [Å] | MoK α 0.71073 |
| Theta Min-Max [°] | 3.3, 28.3 |
| Dataset | -5: 5 ; -12: 11 ; -11: 9 |
| Tot., Uniq. Data, R(int) | 2545, 1617, 0.018 |
| Observed data [I > 2.0 sigma(I)] | 1440 |
| Refinement | |
| Nref, Npar | 1617, 92 |
| R, wR2, S | 0.0332, 0.0870, 0.97 |
| w=1[\s2(Fo2)+(0.0446P)2+0.0578P] | where P=(Fo2+2Fc2)/3 |
| Max. and Av. Shift/Error | 0.00, 0.00 |
| Min. and Max. Resd. Dens. [e[Å3] | -0.21, 0.18 |
Table 1: Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement.
| Bond distances | N1-C5-C1 | 133.2(2) | |
| Bond | Bond Distance | C1-C5-C6 | 121.1(2) |
| S1-C7 | 1.6455(18) | O1-C6-C5 | 108.0(2) |
| C2 -C3 | 1.388(5) | C6-C4-H4 | 122.00 |
| C3-C4 | 1.386(5) | Torsion Angles | |
| O1-C7 | 1.362(3) | Bond | Torsion angles |
| C4-C6 | 1.360(4) | C7-O1-C6-C4 | -179.5(3) |
| N1-C5 | 1.384(4) | C7-O1-C6-C5 | 0.0(3) |
| C5-C6 | 1.381(3) | C6-O1-C7-S1 | 179.41(16) |
| N1-C7 | 1.341(3) | C6-O1-C7-N1 | -0.2(3) |
| C1-C5 | 1.388(4) | C7-N1-C5-C1 | 179.9(3) |
| C1-C2 | 1.386(4 | C7-N1-C5-C6 | -0.3(3) |
| Bond Angles | C5-N1-C7-S1 | -179.25(18) | |
| Bond | Bond angles | C5-N1-C7-O1 | 0.3(3) |
| C6-O1-C7 | 107.97(15) | C2-C1-C5-C6 | 0.8(4) |
| O1-C6-C4 | (128.56(19) | C2-C1-C5-N1 | -179.4(3) |
| C5-N1-C7 | 110.45(19) | C5-C1-C2-C3 | -0.6(5) |
| O1-C7-N1 | 107.90(17) | C1-C2-C3-C4 | -0.1(5) |
| S1-C7-O1 | 121.75(19) | C2-C3-C4-C6 | 0.5(5) |
| S1-C7-N1 | 130.4(2) | C3-C4-C6-C5 | -0.2(5) |
| C2-C1-C5 | 116.1(3) | C3-C4-C6-O1 | 179.2(3) |
| C1-C2-C3 | 121.7(3) | N1-C5-C6-O1 | 0.2(3) |
| C2-C3-C4 | 121.9(3) | C1-C5-C6-C4 | -0.4(4) |
| C3-C4-C6 | 115.8(3) | N1-C5-C6-C4 | 179.7(3) |
| N1-C5-C6 | 105.7(2) | C1-C5-C6-O1 | -180.0(2) |
Table 2: Selected geometrical parameters (Å).
| D—H...A | D—H | H...A | D..A | D—H...A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1...S1i | 0.861(15) | 1.990(15) | 2.8471(16) | 173.3(16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) -x, -1/2+y, -z
Table 3: Hydrogen Bonding Geometry for title crystal (Å).
Results and Discussion
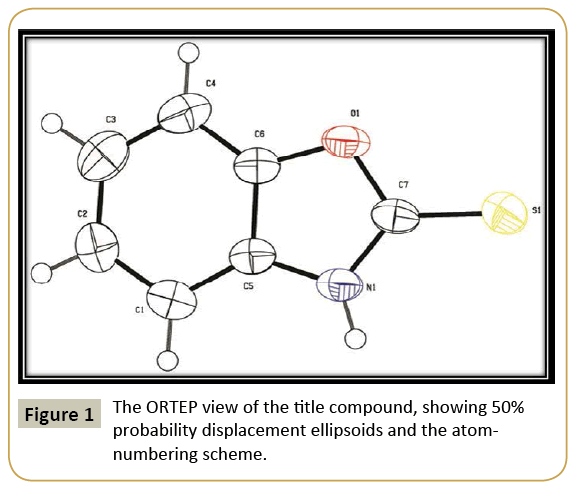
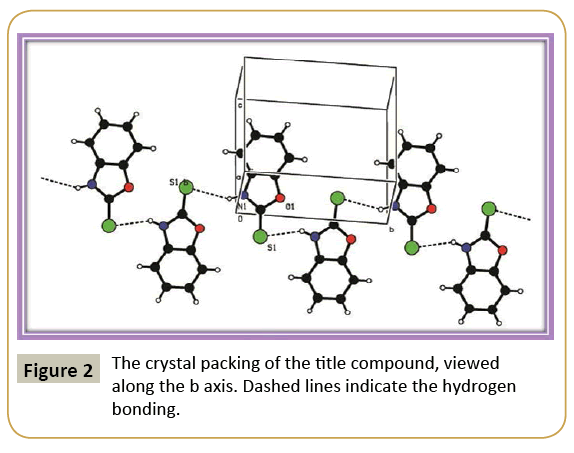
Figure 1 shows the ORTEP plot of the molecule drawn at 50% probability ellipsoid level with atom numbering scheme. Figure 2 shows the packing of compound viewed along the ‘b’ axis. The asymmetric unit contains one 2-mercaptobenzoxazole and crystallized in the monoclinic system, the systematic absences permitting space group P21 was assumed and confirmed by the analysis. The molecules are held together by intermolecular N1- --H1…S1 hydrogen bond (Table 3) forming a one-dimensional network parallel to the ab plane. H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93Å/ N–H = 0.86 Å) and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Conclusion
The crystal structure of 2-mercaptobenzoxazole has been investigated in detail. The molecular structure of the compound is stabilized by strong inter-molecular hydrogen bond. The packing motif of the self-complementary hydrogen bonded 2-mercaptobenzoxazole to form a 1D chain.
Acknowledgements
P. Sivajeyanthi and K. Balasubramani thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST-SERB), Grant No. SB/FT/CS– 058/2013, New Delhi, India for financial support and also thank for using the Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Facility (SAIF) at STIC, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin.
CCDC Nos. 1450406 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Director, CCDC, 12 Union Road, Cambridge, CB2 1EZ, UK, Fax: +44 1223 366 033, E-mail: deposit@ccdc.ac.uk or https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/conts/retrieving.html.
References
- Raper ES (1994) Copper complexes of heterocyclic thioamides and related ligands. Coord Chem Rev. pp: 91-129.
- Castano CV, Calvo H, Sánchez A, Casas S, Sordo J (1991) J Organomet Chem 417: 327.
- Seidel P (1890) J Prakt chem 42: 445-457.
- Desai RD, Hunter RF, Khalidi ARK (1934) J Chem Soc. pp: 1186-1190.
- Marabini AM, Barbaro M, Alesse V (1991) New reagents in sulphide mineral flotation. Int J Miner Process 33: 291-306.
- Contini G, Ciccioli A, Cozza C, Barbaro M, Marabini AM (1997) Infrared study of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole and two of its derivatives adsorbed on PbS. Int J Miner Process 51: 283-291.
- Bruker (2001) SMART, SAINT, SHELXTL and SADABS. Bruker Axs Inc., Madison, WI, USA.
- Bruker (2004) APEX2, SAINT-plus and SADABS. BRUKER AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA.
- Sheldrick GM (1997) SHELXS97 and SHELXL97. University of Gottingen, Germany.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences